Zero Knowledge Proofs, Enhancing Privacy and Security in Blockchain
Innovation Non-Stop
As blockchain technology continues to revolutionize various industries, the need for privacy and security has become increasingly paramount.
One powerful tool addressing these concerns is Zero Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs). In this article, we’ll delve into what ZKPs are, how they work, and their significance in blockchain technology.
https://ethereum.org/en/zero-knowledge-proofs/
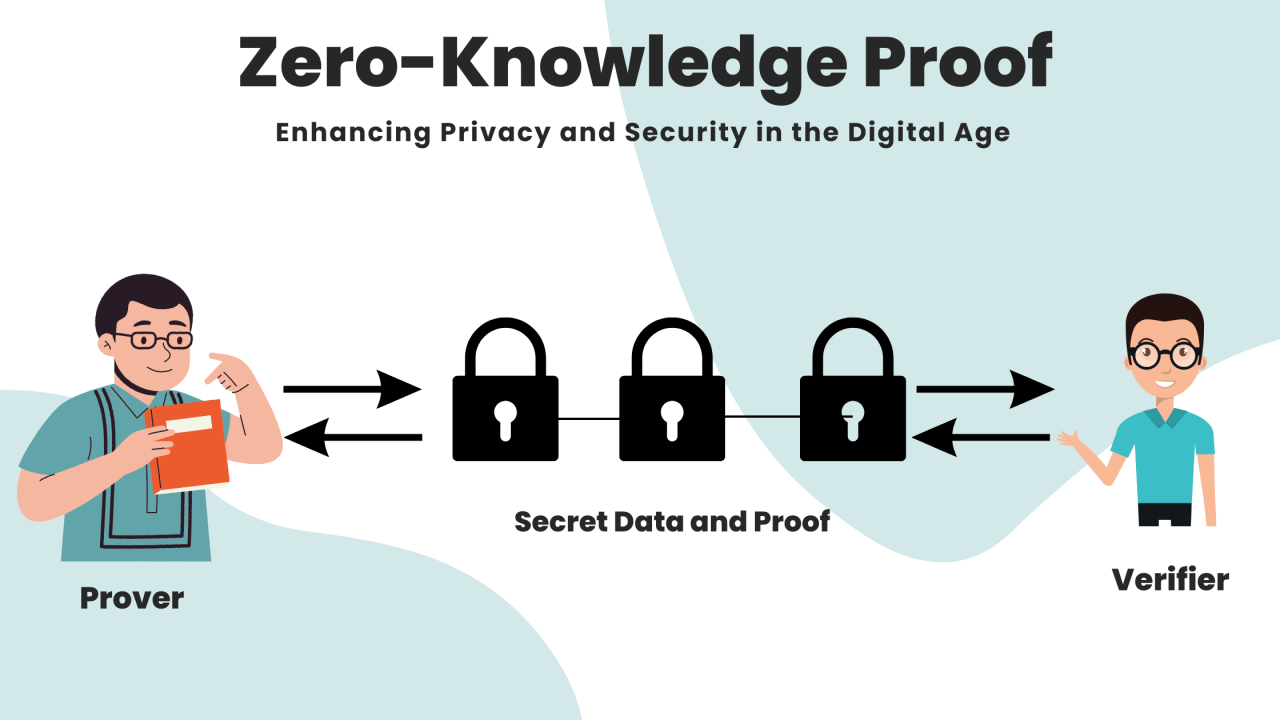
Zero Knowledge Proofs are cryptographic protocols that enable one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true without revealing any additional information beyond the validity of the statement itself. In simpler terms, ZKPs allow individuals to authenticate data without disclosing the data itself.
The concept behind ZKPs can be illustrated through a basic example known as the “Ali Baba’s Cave” scenario. Imagine a scenario where Ali Baba wants to prove to a guard that he knows the secret passphrase to access a cave without revealing the passphrase itself. Through a Zero Knowledge Proof, Ali Baba can demonstrate his knowledge of the passphrase by performing a series of actions inside the cave that only someone with the correct passphrase would know, without disclosing the passphrase itself.
In the context of blockchain technology, ZKPs enable users to prove ownership or knowledge of specific information without revealing sensitive data such as private keys or transaction details.
This is particularly valuable in decentralized finance (DeFi), where preserving financial privacy is crucial.
Applications of Zero Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain:
- Privacy Coins: Zero Knowledge Proofs are fundamental to the development of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Zcash (ZEC) and Monero (XMR). By using ZKPs, users can transact privately, ensuring that transaction amounts, sender addresses, and recipient addresses remain confidential on the blockchain.
- Authentication and Identity Verification: ZKPs can be leveraged for identity verification and authentication without compromising users’ privacy. This is especially relevant in applications where sensitive personal information needs to be verified without being shared, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
- Secure Voting Systems: Zero Knowledge Proofs can enhance the security and integrity of voting systems by allowing voters to prove that their votes were counted correctly without revealing their actual votes. This ensures anonymity and prevents coercion or vote manipulation.
- Scalable Blockchain Solutions: ZKPs can also contribute to scalability solutions like zk-Rollups and zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge), which allow for efficient transaction processing and validation without compromising on-chain privacy.
Zero Knowledge Proofs represent a groundbreaking advancement in cryptography, offering unparalleled privacy and security guarantees in blockchain technology. By