An Easy Guide to Understanding zkEVM and Its Key Concepts
Innovation is zkEVM
As blockchain technology evolves, new innovations aim to make it more efficient, scalable, and private. One such innovation is zkEVM, a powerful solution that integrates Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). In this article, we’ll break down the key concepts behind zkEVM, making it easy for anyone, even those new to the blockchain space, to understand.
- What are Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)?: Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) are cryptographic techniques that allow one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true without revealing any details about the statement itself. Imagine you know the answer to a puzzle, and you want to prove that you know it without actually giving away the answer. That’s essentially what ZKPs do.
In the context of zkEVM, ZKPs are used to verify that computations on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) are correct without having to re-run them. This not only ensures that transactions are secure but also makes the process faster and more private.
- What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?: The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the environment where all Ethereum accounts and smart contracts exist and operate. It’s like the engine that runs the Ethereum blockchain, executing the smart contract code and handling transactions.
zkEVM is a version of the EVM that incorporates Zero-Knowledge Proofs. This integration allows zkEVM to perform the same tasks as the regular EVM but in a way that is more scalable and private. It’s like upgrading the engine of a car to make it faster and more efficient.
- What is Scalability in Blockchain?: Scalability refers to a blockchain’s ability to handle an increasing number of transactions and data without slowing down or becoming too expensive. A scalable blockchain can grow and support more users without compromising performance.
zkEVM enhances scalability by moving some of the work off the main Ethereum network (known as the mainnet) and onto a secondary layer (Layer 2). This secondary layer handles the heavy lifting, while ZKPs ensure everything is done correctly. The result? Faster, cheaper transactions that don’t clog up the main network.
- What Does Privacy Mean in Blockchain?: Privacy in blockchain ensures that details of transactions—like who’s sending money, how much they’re sending, and who’s receiving it—are hidden or protected from the public. Using ZKPs, zkEVM can conduct transactions without revealing all the details on the public blockchain. This means users can enjoy the benefits of blockchain technology without compromising their privacy.
- What are Layer 2 Solutions?: Layer 2 solutions are additional systems built on top of a blockchain’s main network (Layer 1) to improve its performance. Think of it as building an express lane on a busy highway—traffic moves faster because some cars (transactions) take the faster route.
- Relevance to zkEVM: zkEVM operates as a Layer 2 solution, meaning it runs on top of Ethereum’s main network. It takes on some of the computational work, making the whole system more efficient while still relying on Ethereum’s security and decentralization.
- What Does Compatibility with Ethereum Mean?: Compatibility with Ethereum means that a system can run existing Ethereum smart contracts and interact with Ethereum-based applications without requiring any changes.
- Relevance to zkEVM: zkEVM is designed to be fully compatible with the existing EVM. This means all the smart contracts and applications that work on Ethereum will also work on zkEVM, but with added benefits like scalability and privacy.
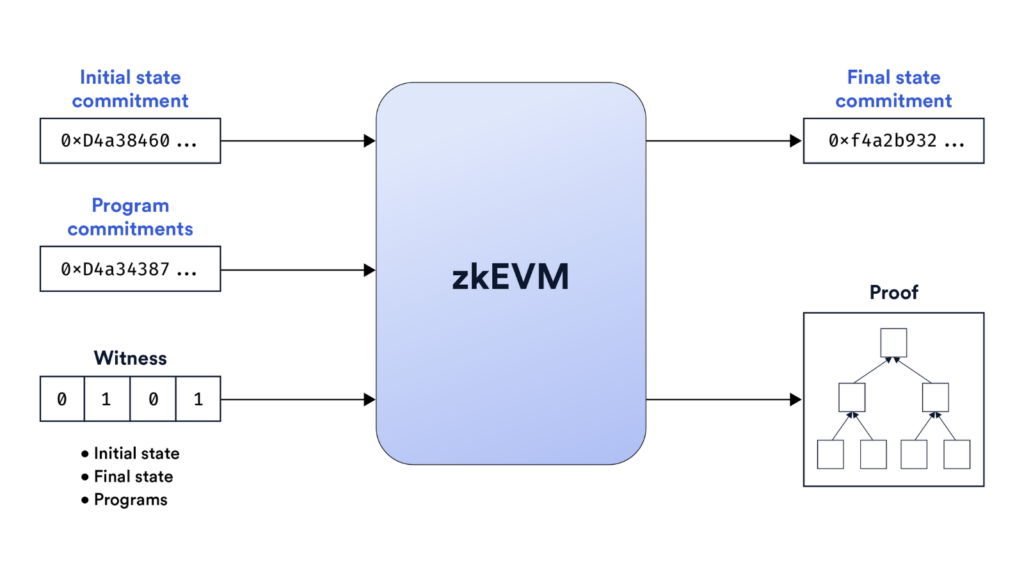
zkEVM generates these proofs to show that transactions and computations are correct. The Ethereum mainnet then verifies these proofs, ensuring everything is secure without having to redo the computations, saving time and resources.
By offloading computations to Layer 2 and using ZKPs, zkEVM reduces the gas costs associated with transactions. This makes it cheaper for users to interact with the blockchain, which is a huge benefit, especially as Ethereum continues to grow.
- What is Proof Generation and Verification?: In zkEVM, proof generation is the process of creating a Zero-Knowledge Proof that confirms a computation (like a transaction) is correct. Proof verification is the process of checking that this proof is valid.
- What is Gas Efficiency?: Gas in Ethereum is a fee you pay to execute transactions or run smart contracts on the network. Gas efficiency refers to minimizing these costs.
Understanding these concepts helps you grasp how zkEVM integrates Zero-Knowledge Proofs with the Ethereum Virtual Machine to create a more scalable, private, and efficient decentralized computation platform. By leveraging the strengths of both ZKPs and Ethereum, zkEVM represents a significant step forward in making blockchain technology more accessible and practical for everyday use. Whether you’re new to blockchain or looking to deepen your understanding, zkEVM is a promising development that could shape the future of decentralized applications.