Understanding the Travel Rule and Its Impact on European Customers and Non-European Exchanges
Europe, regulations leader and destroying Innovation
In recent years, the rapid growth of the cryptocurrency industry has prompted governments and regulatory bodies worldwide to establish frameworks that ensure compliance, enhance transparency, and combat illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorism financing. One significant regulation in this context is the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF) “Travel Rule.” For European customers and exchanges, including those operating outside Europe, the Travel Rule has brought both challenges and opportunities. This article explores the Travel Rule, its impact on European customers, and how it affects non-European exchanges.
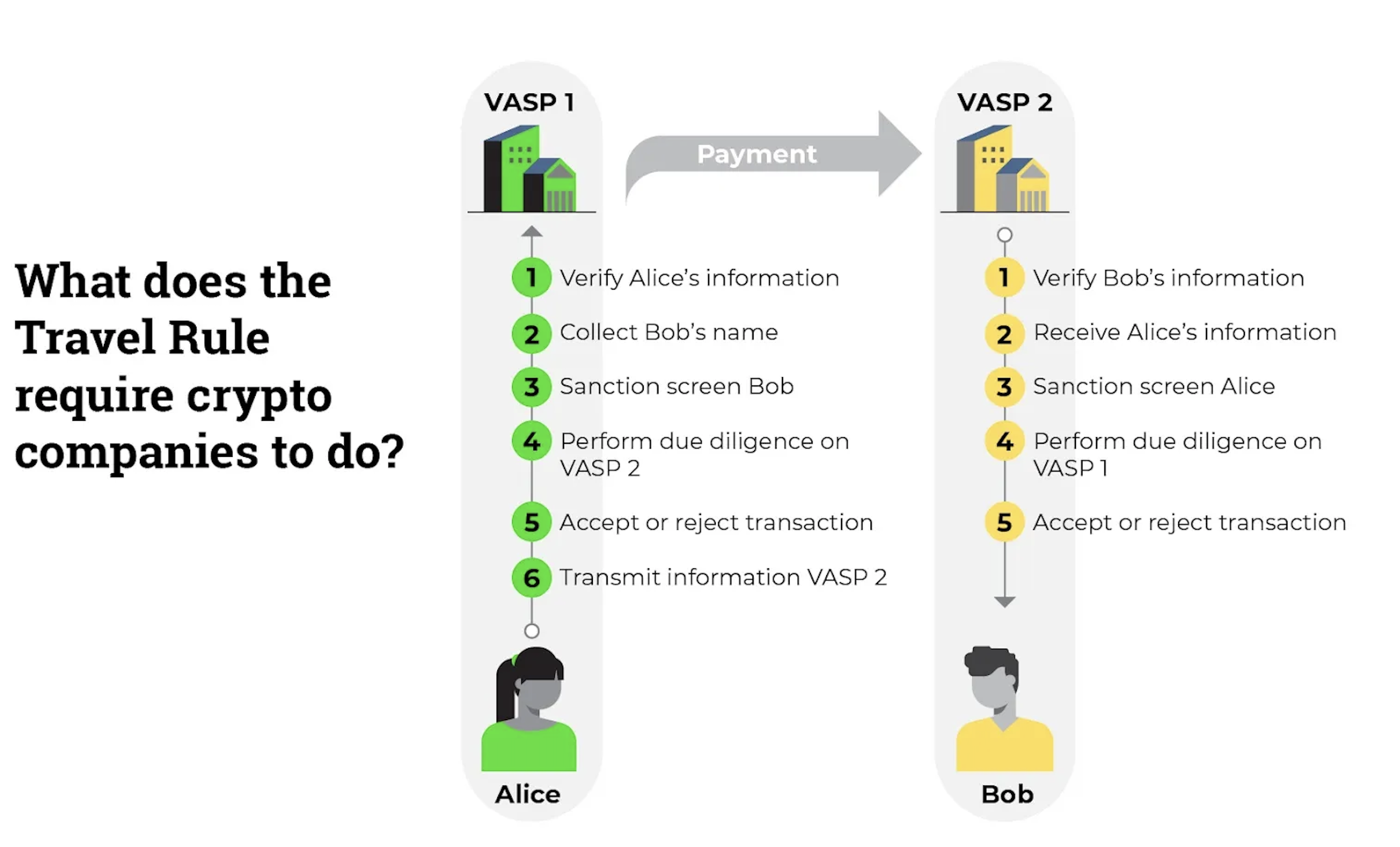
The Travel Rule, formally known as Recommendation 16 of the FATF guidelines, requires Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), such as cryptocurrency exchanges, to share specific customer information when transferring cryptocurrencies above a certain threshold. This information includes:
- Originator Information: The sender’s name, account number (or unique identifier), and address (or alternative identifiers such as national ID or date of birth).
- Beneficiary Information: The recipient’s name and account number (or unique identifier).
The goal of the Travel Rule is to bring cryptocurrency transactions in line with traditional financial systems’ anti money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) requirements.
For customers in the European Union (EU), compliance with the Travel Rule became mandatory with the introduction of the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation and updates to the EU’s AML directives. These regulations aim to ensure that cryptocurrency transactions are transparent and traceable across the bloc. Here’s how this affects European customers:
- Increased Transparency: European customers must provide additional personal information when initiating or receiving cryptocurrency transactions above the specified threshold (e.g., €1,000 in the EU).
- Reduced Privacy: Many crypto enthusiasts value the privacy associated with digital assets. The Travel Rule’s requirements for data sharing can create concerns about how personal information is stored, used, and protected.
- Higher Costs: Exchanges and VASPs incur operational costs to implement Travel Rule compliance systems. These costs may be passed on to customers in the form of higher transaction fees.
- Restricted Services: Some European exchanges may limit transactions with non-compliant VASPs or jurisdictions that do not enforce the Travel Rule, potentially reducing the availability of services for customers.
Exchanges based outside Europe that serve European customers are also affected by the Travel Rule. They must implement mechanisms to comply with European regulations or risk losing access to the European market. Key implications include:
- Regulatory Compliance Challenges: Non-European exchanges must navigate varying compliance requirements across different jurisdictions, including the EU. This often involves updating internal systems, training staff, and integrating new tools to meet data-sharing standards.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Non-European exchanges must establish partnerships with European VASPs to facilitate the secure transfer of customer information. Failure to comply can result in transaction delays or refusal.
- Customer Base Restrictions: Some exchanges opt to exclude European customers entirely to avoid the complexities and costs of compliance, which can limit options for European users.
- Competitive Advantage: Exchanges that proactively comply with the Travel Rule can position themselves as trusted platforms in the global market, attracting both European and non-European customers seeking secure and compliant services.
While the Travel Rule enhances transparency and reduces risks of illicit activities, it also raises concerns about privacy and data security. European regulators and VASPs must ensure that personal information shared under the Travel Rule is handled securely and used only for its intended purpose. Robust encryption, data anonymization techniques, and adherence to GDPR principles are critical to balancing compliance with privacy.
The FATF’s Travel Rule has introduced significant changes to the cryptocurrency landscape, particularly for European customers and exchanges outside the region. While the regulation enhances transparency and combats financial crime, it also presents challenges related to privacy, operational costs, and cross-border collaboration. As the crypto industry continues to evolve, striking a balance between compliance and user privacy will remain a key priority for regulators, exchanges, and customers alike.